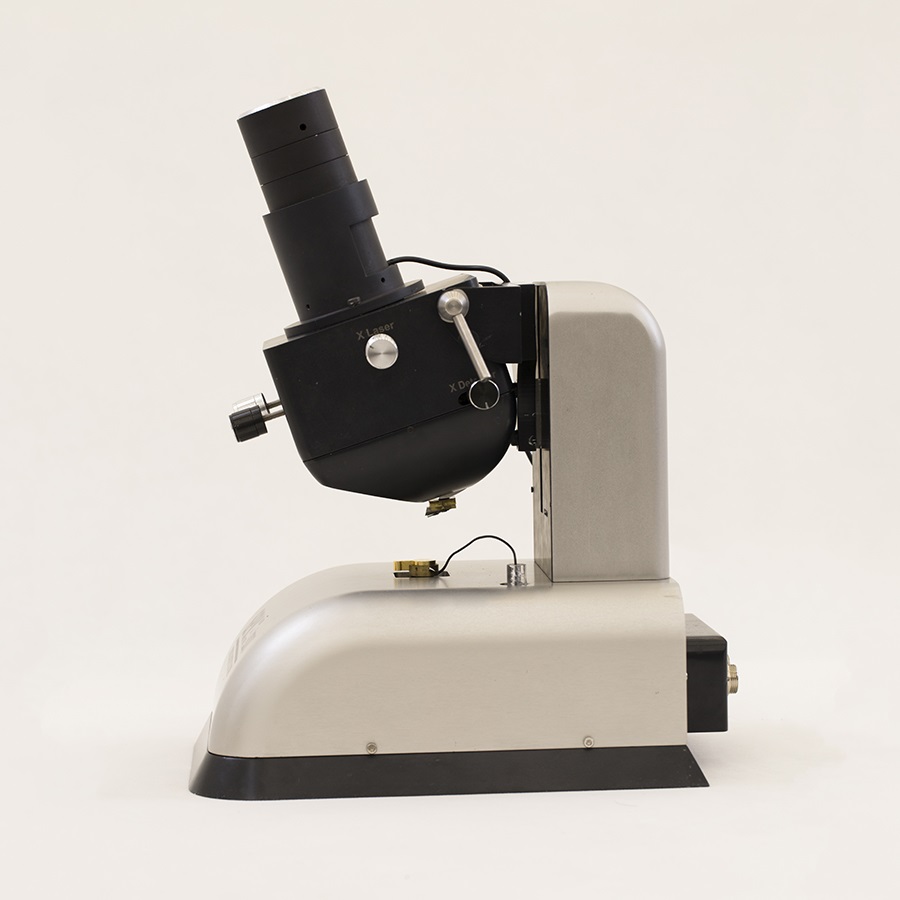
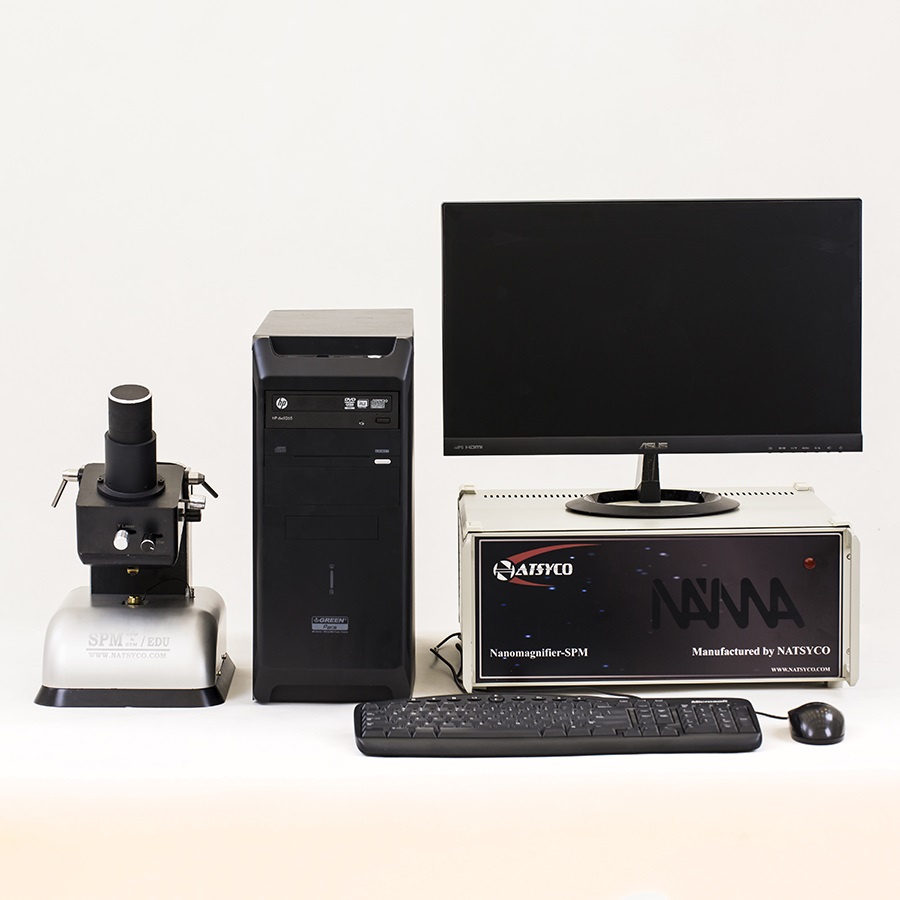




Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
Scanning probe microscopy (SPM) is a branch of microscopy that forms images of surfaces using a physical probe that scans the specimen. SPM was founded with the invention of the scanning tunneling microscope in 1981.

Applications
- Atomic-scale imaging of solid surfaces
- Research on catalytic agents
- Surface imaging of conductive and semi-conductive surfaces
- Imaging of DNA, RNA and …
- Measuring the smoothness of optical surfaces
- Determining the magnetic and electric properties

Special Features
- Imaging based on atomic force
- Camera view for both sample and cantilever and /tip (in STM mode)
- Anti-vibration table with damper
- Simultaneous readouts of topography and phase domain for both semi- and non-contact materials
- Electronic ON and OFF switch for camera

Technical Specifications
- AFM mode:
- Maximum Z-range: 5 µm
- Z direction resolution: 0.07 nm
- XY direction resolution: 0.25 nm
- Imaging modes: contact (fixed height and force) and semi-contact and non-contact
- STM mode:
- Maximum Z-range: 5 µm
- Maximum XY-range: 20 µm
- Z direction resolution: 0.07 nm
- XY direction resolution: 0.25 nm
- Motorized sample movement
- Imaging modes: constant current, constant height
